Sterilization of ready to eat meal: a key link to ensure food safety
ready to eat meal will be exposed to various microorganisms during processing. From the picking and transportation of raw materials to the processing and packaging of ready to eat meal, there is a risk of contamination by bacteria, fungi, viruses, etc. For example, fresh vegetables may carry harmful bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella, and meat raw materials may carry heat-resistant bacteria such as Bacillus. If they are not effectively sterilized, these microorganisms will multiply in large numbers during the storage and consumption of ready to eat meal, causing health problems such as food poisoning for consumers.
According to national food safety standards, microbial indicators in food must be controlled within a safe range. Sterilization of ready to eat meal can ensure that it meets these strict standards, reduce the probability of foodborne diseases, and protect the health of consumers.
The growth and reproduction of microorganisms is one of the main reasons for the deterioration of ready to eat meal. Through sterilization treatment, the activity of microorganisms can be effectively killed or inhibited, thereby extending the shelf life of ready to eat meal.
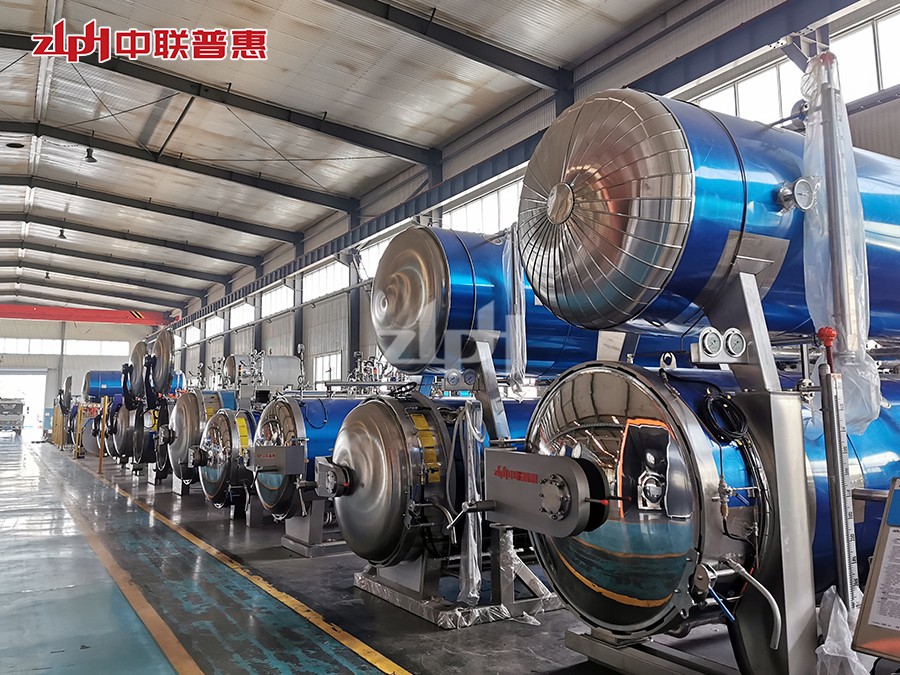
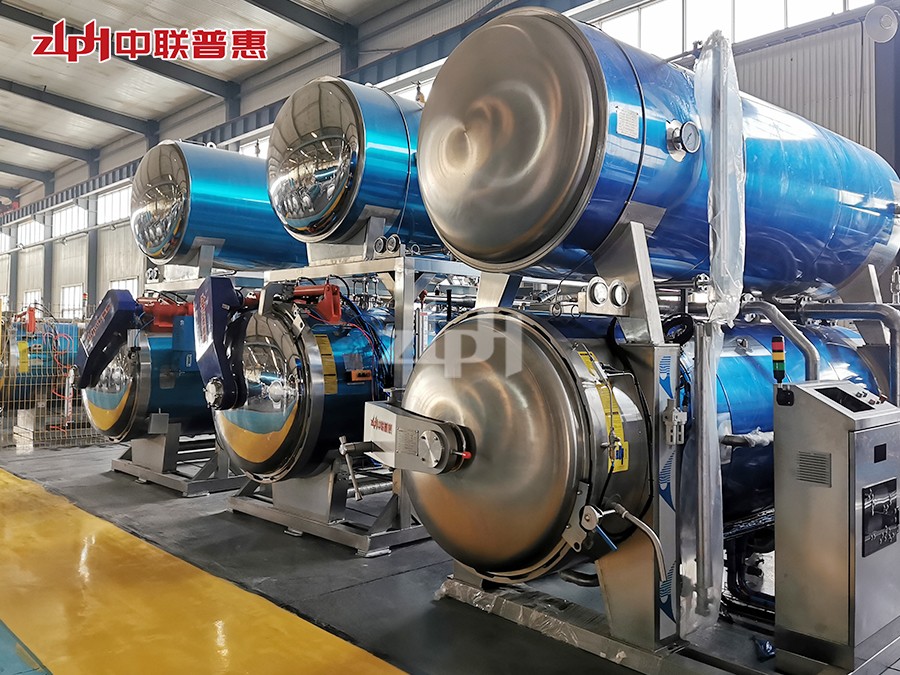
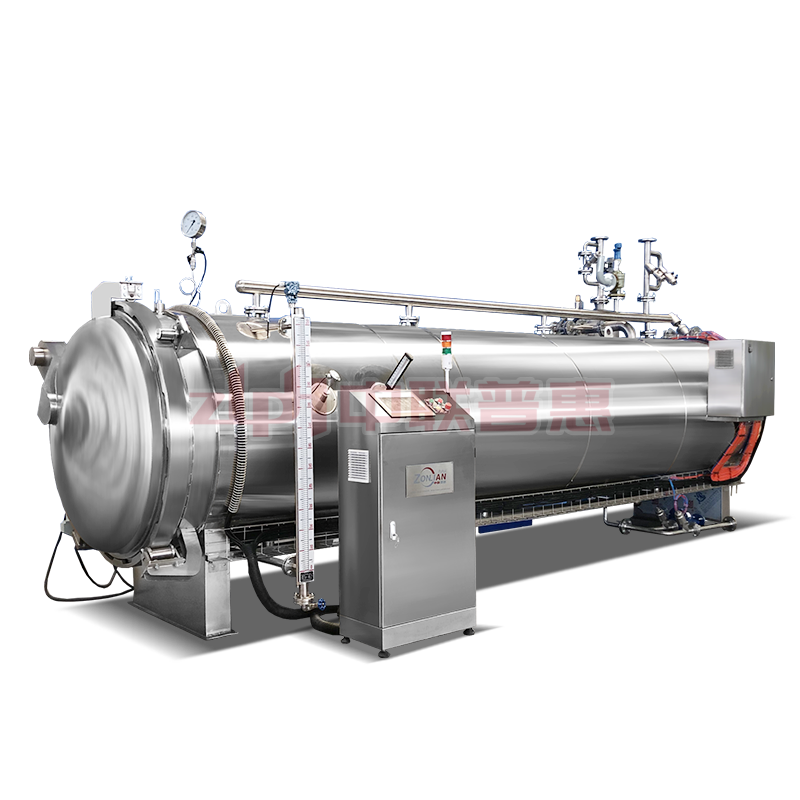
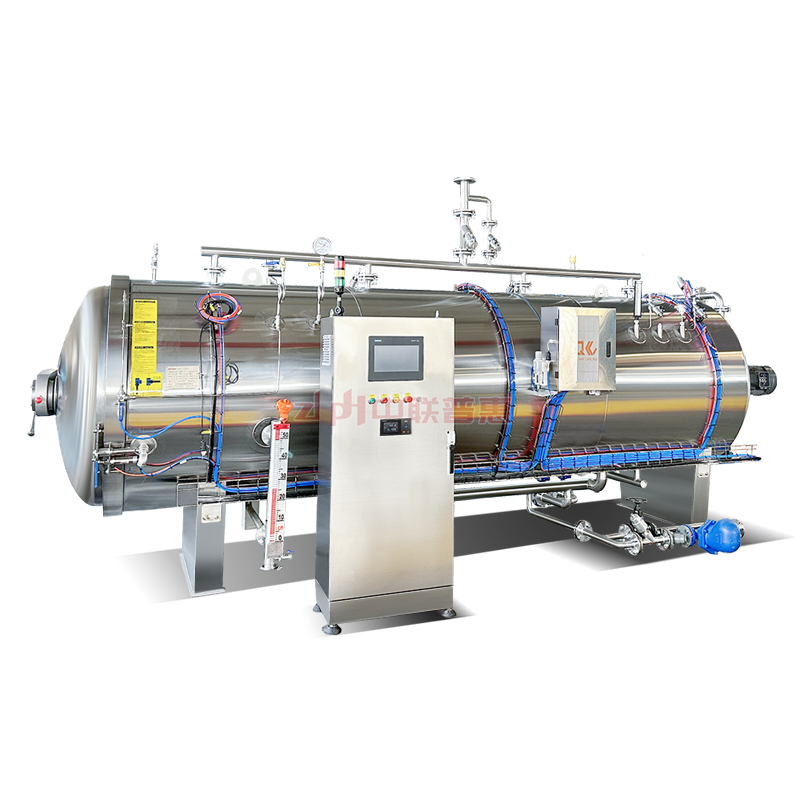
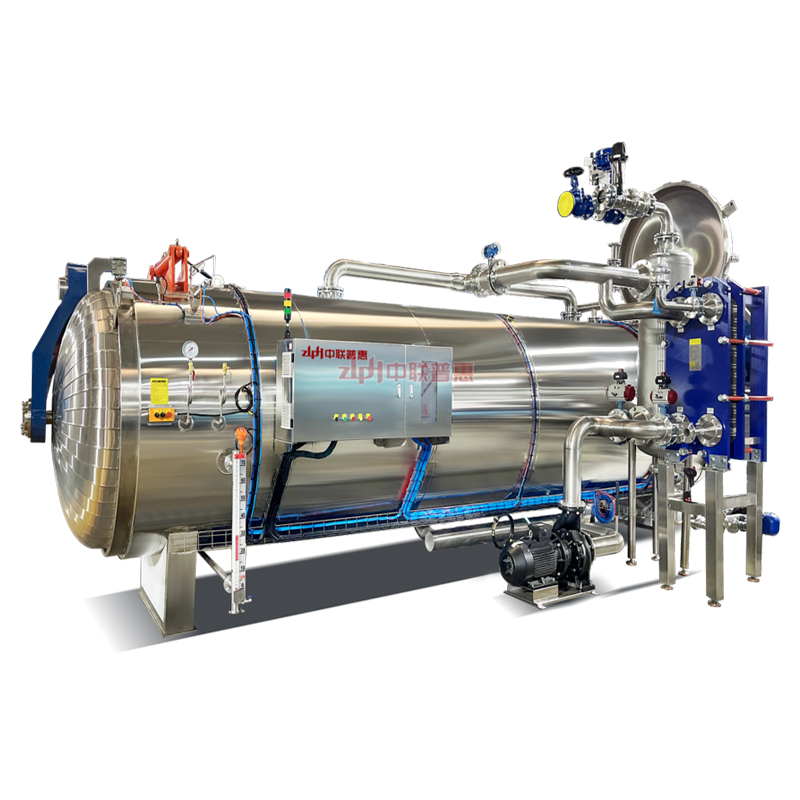
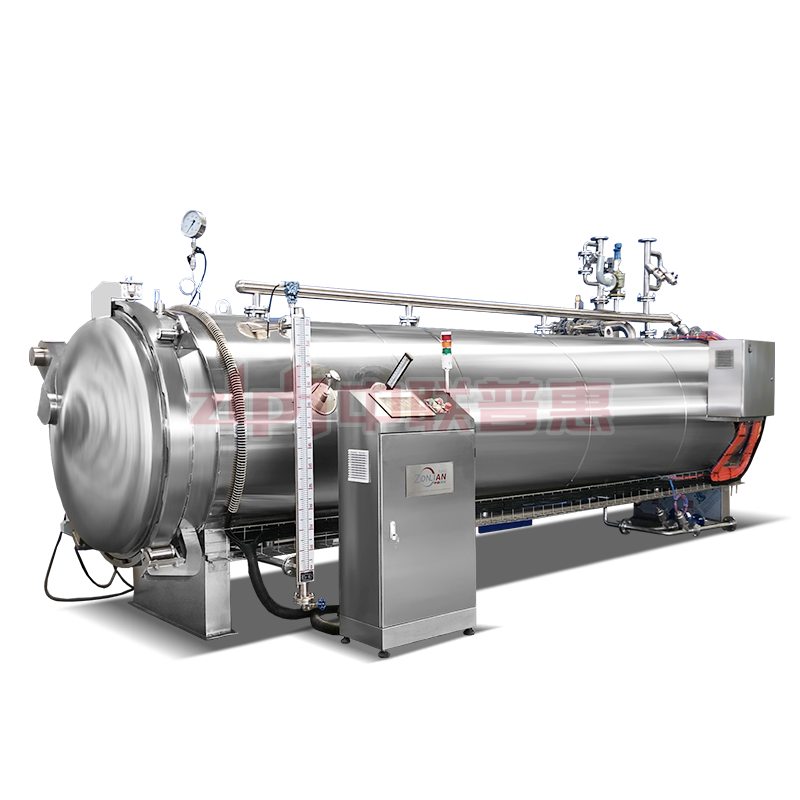
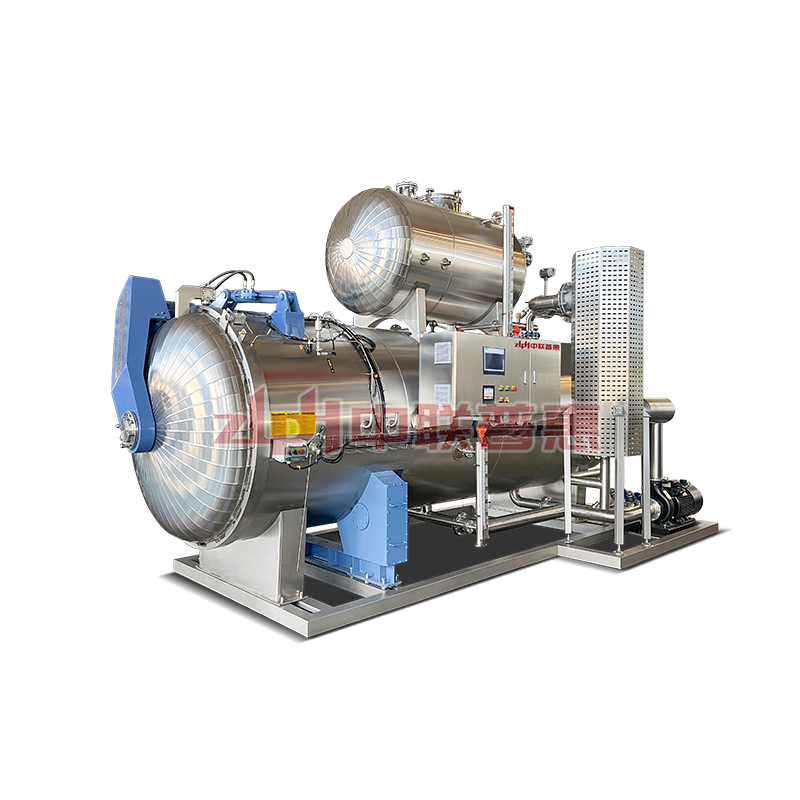
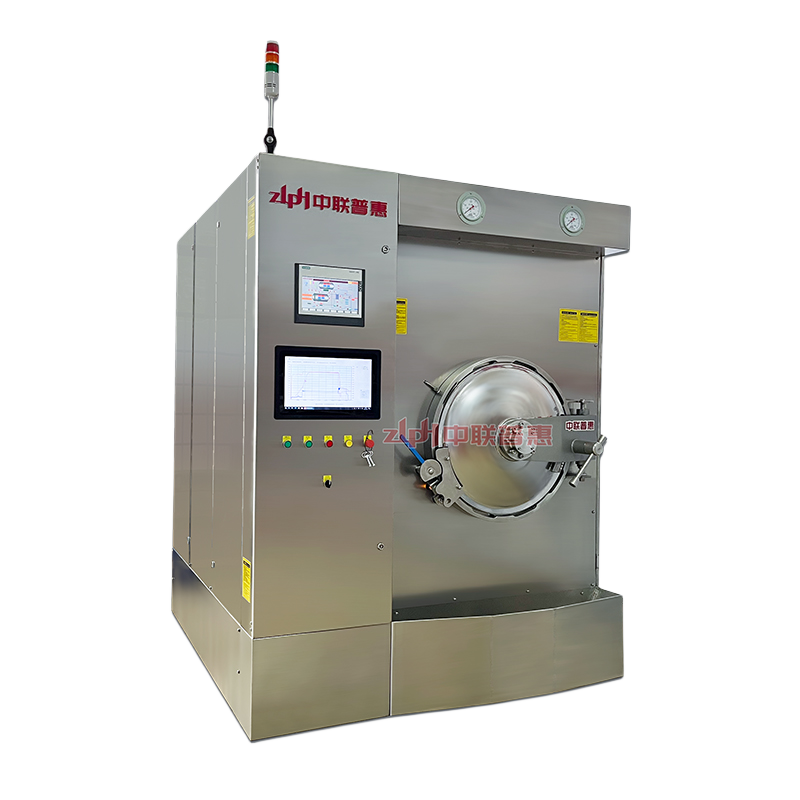
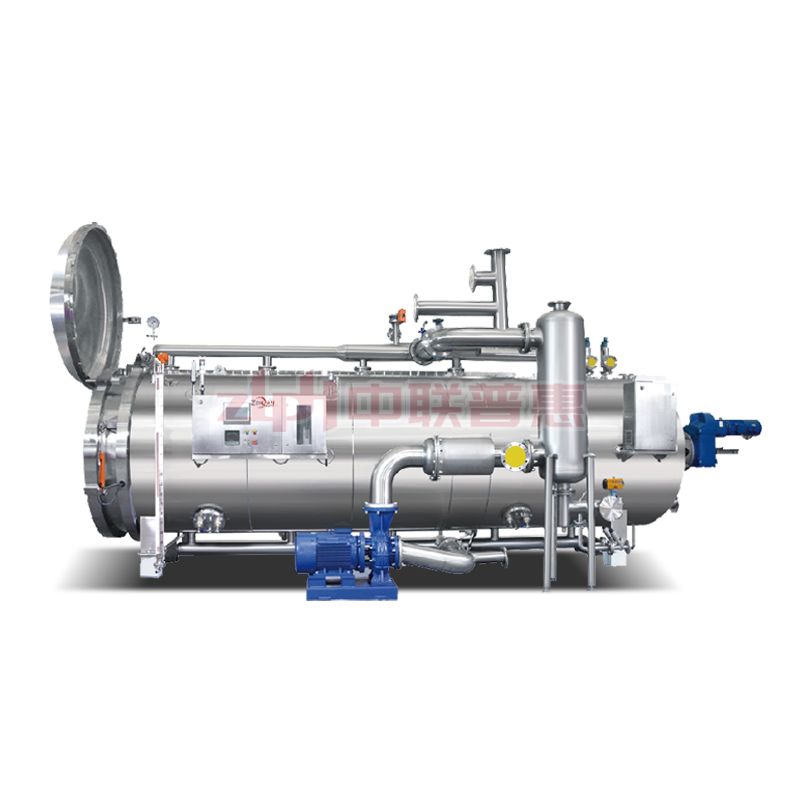
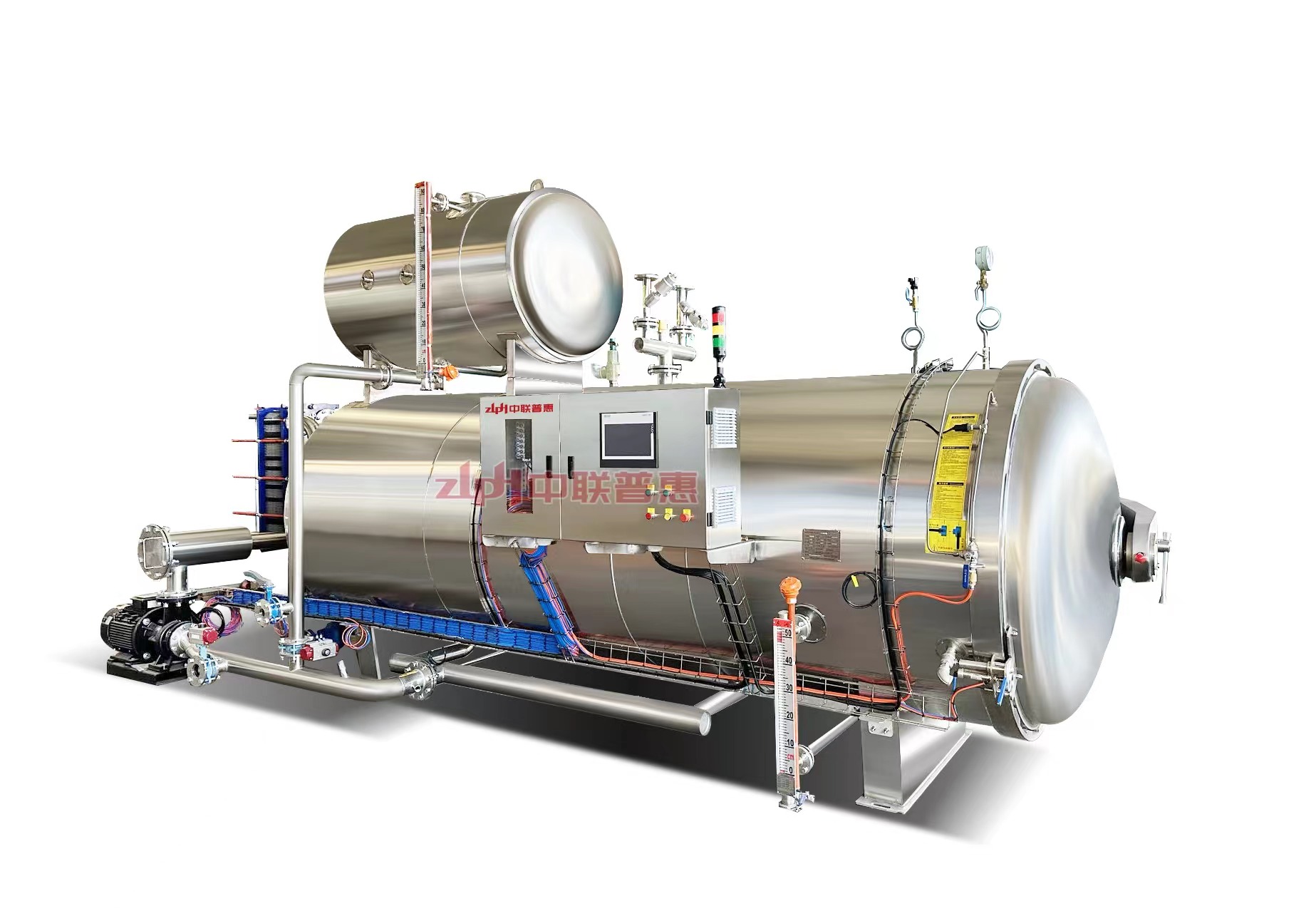
Principle: Use the heat of high-temperature steam to kill microorganisms. Steam can penetrate the packaging of ready to eat meal (if it is a breathable packaging) or form a high-temperature environment on the surface of ready to eat meal. Generally, the temperature is above 100℃, for example, high-temperature steam at 121℃ can effectively kill most microorganisms including Bacillus.
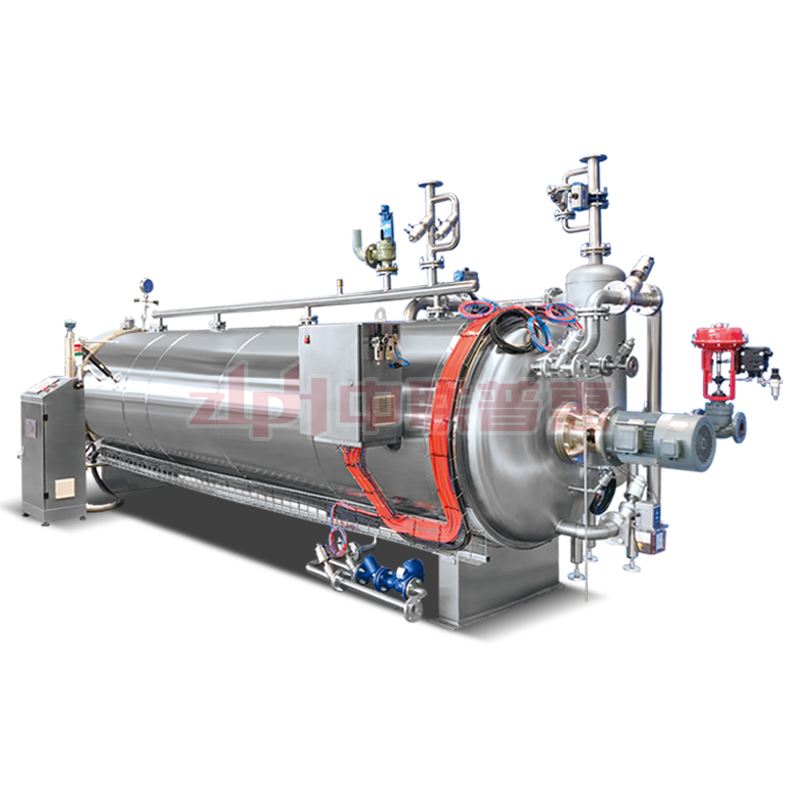
Principle: After the ready to eat meal is packaged, it is placed in a high-temperature sterilizer and sterilized by the heat transferred by hot water. The temperature of hot water is usually around 121℃. The time is adjusted according to the type of ready to eat meal and the packaging form, and it usually lasts for 15-30 minutes. This method is relatively mild and suitable for some ready to eat meal that is sensitive to temperature, such as vegetable ready to eat meal containing nutrients that are easily destroyed by high temperature.